| dc.contributor | Vall d'Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus |
| dc.contributor.author | Porcu, Luca |
| dc.contributor.author | Agbor-Tarh, Dominique Akong |
| dc.contributor.author | CINIERI, Saverio |
| dc.contributor.author | Franzoi, Maria Alice |
| dc.contributor.author | Di Cosimo, Serena |
| dc.contributor.author | Saura Manich, Cristina |
| dc.contributor.author | De Santis, Maria Carmen |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2021-09-10T10:04:01Z |
| dc.date.available | 2021-09-10T10:04:01Z |
| dc.date.issued | 2020-10-27 |
| dc.identifier.citation | Di Cosimo S, Porcu L, Agbor-tarh D, Cinieri S, Franzoi MA, De Santis MC, et al. Effect of body mass index on response to neo-adjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer: an exploratory analysis of the NeoALTTO trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 27;22:115. |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1465-542X |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11351/6297 |
| dc.description | Body mass index; HER2-positive breast cancer; Neo-adjuvant treatment |
| dc.description.abstract | Background
Obesity is a risk factor for breast cancer (BC) development, recurrence, and death. In view of this, we aimed to investigate the clinical value of obesity in BC patients treated with anti-HER2 therapies in the NeoALTTO trial, which randomized 455 patients to neo-adjuvant lapatinib, trastuzumab, or their combination plus paclitaxel.
Methods
Patients were classified according to their basal body mass index (BMI) into underweight (< 18.5 kg/m2), normal (≥ 18.5; < 25 kg/m2), overweight (≥ 25; < 30 kg/m2), and obese (≥ 30 kg/m2) WHO categories. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed using BMI as a categorical variable. Pathological complete response (pCR) and event-free survival (EFS) were the NeoALTTO primary and secondary outcomes, respectively.
Results
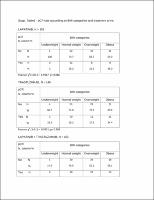
Among 454 patients analyzed, 14 (3%), 220 (48%), 137 (30%), and 83 (18%) were classified as underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese, respectively; 231 (51%) and 223 (49%) had hormone receptor (HR)-positive and HR-negative primary tumors; 160 (35%) achieved pCR. In the overall patient population, no association was found between BMI groups and pCR, as we reported pCR rates of 57.1%, 35%, 30.7%, and 39.8% in underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese cases, respectively. In contrast, in HR-positive tumors, overweight or obesity was generally associated with decreased likelihood of achieving a pCR independently of other clinical variables, including planned surgery, nodal status, and tumor size (odds ratio [OR] = 0.55, 95%CI 0.30–1.01, as compared to normal or underweight; p = 0.053); notably, no differential effect of BMI with respect to pCR was observed in HR-negative cases (odds ratio [OR] = 1.30, 95%CI 0.76–2.23, as compared to normal or underweight; p = 0.331), resulting in a statistically significant interaction between BMI and HR status (p = 0.036). There was no association between BMI and EFS neither in the overall nor in the HR-positive population, but this analysis was under-powered.
Conclusions
NeoALTTO patients overweight or obese at baseline and with HR-positive primary BC appeared less likely to achieve pCR after neo-adjuvant anti-HER2 therapies. This finding paves the way to future research in targeting the interplay between HER2/HR signaling and metabolism. |
| dc.language.iso | eng |
| dc.publisher | BMC |
| dc.relation.ispartofseries | Breast Cancer Research;22 |
| dc.rights | Attribution 4.0 International |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ |
| dc.source | Scientia |
| dc.subject | Mama - Càncer - Tractament |
| dc.subject | Obesitat - Fisiologia patològica |
| dc.subject.mesh | Breast Neoplasms |
| dc.subject.mesh | Neoadjuvant Therapy |
| dc.subject.mesh | Overweight |
| dc.subject.mesh | /physiopathology |
| dc.title | Effect of body mass index on response to neo-adjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer: an exploratory analysis of the NeoALTTO trial |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1186/s13058-020-01356-w |
| dc.subject.decs | neoplasias de la mama |
| dc.subject.decs | tratamiento neoadyuvante |
| dc.subject.decs | sobrepeso |
| dc.subject.decs | /fisiopatología |
| dc.relation.publishversion | https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-020-01356-w |
| dc.type.version | info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion |
| dc.audience | Professionals |
| dc.contributor.organismes | Institut Català de la Salut |
| dc.contributor.authoraffiliation | [Di Cosimo S] Biomarkers Unit, Department of Applied Research and Technological Development, Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, via G.A. Amadeo 42, 20133 Milano, Italy. [Porcu L] Laboratory of Methodology for Clinical Research, Department of Oncology, Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS, Milano, Italy. [Agbor-tarh D] Frontier Science (Scotland) Ltd, Kincraig, UK. [Cinieri S] San Antonio Perrino Hospital, Brindisi, Italy. [Franzoi MA] Institut Jules Bordet and l’Universitè Libre de Bruxelles (U.LB), Brussels, Belgium. [De Santis MC] Radiation Oncology, Fondazione IRSCCS Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori, Milano, Italy. [Saura C] Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), Barcelona, Spain |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 33109233 |
| dc.identifier.wos | 000589613500004 |
| dc.rights.accessrights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess |