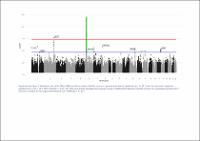
| dc.contributor | Vall d'Hebron Barcelona Hospital Campus |
| dc.contributor.author | Rothwell, Simon |
| dc.contributor.author | Amos, Christopher |
| dc.contributor.author | Miller, Frederick |
| dc.contributor.author | Rider, Lisa |
| dc.contributor.author | Lundberg, Ingrid |
| dc.contributor.author | Gregersen, Peter |
| dc.contributor.author | Selva-O'Callaghan, Albert |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2023-06-12T10:45:51Z |
| dc.date.available | 2023-06-12T10:45:51Z |
| dc.date.issued | 2023-06 |
| dc.identifier.citation | Rothwell S, Amos CI, Miller FW, Rider LG, Lundberg IE, Gregersen PK, et al. Identification of Novel Associations and Localization of Signals in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Using Genome-Wide Imputation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Jun;75(6):1021–7. |
| dc.identifier.issn | 2326-5205 |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11351/9719 |
| dc.description | Miopatías inflamatorias idiopáticas; Genoma |
| dc.language.iso | eng |
| dc.publisher | Wiley |
| dc.relation.ispartofseries | Arthritis & Rheumatology;75(6) |
| dc.rights | Attribution 4.0 International |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ |
| dc.source | Scientia |
| dc.subject | Malalties autoimmunitàries - Aspectes genètics |
| dc.subject | Músculs - Malalties - Aspectes genètics |
| dc.subject.mesh | Autoimmune Diseases |
| dc.subject.mesh | /genetics |
| dc.subject.mesh | Myositis |
| dc.subject.mesh | Genetic Predisposition to Disease |
| dc.title | Identification of Novel Associations and Localization of Signals in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies Using Genome-Wide Imputation |
| dc.type | info:eu-repo/semantics/article |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1002/art.42434 |
| dc.subject.decs | enfermedades autoinmunes |
| dc.subject.decs | /genética |
| dc.subject.decs | miositis |
| dc.subject.decs | predisposición genética a la enfermedad |
| dc.relation.publishversion | https://doi.org/10.1002/art.42434 |
| dc.type.version | info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion |
| dc.audience | Professionals |
| dc.contributor.organismes | Institut Català de la Salut |
| dc.contributor.authoraffiliation | [Rothwell S] Centre for Genetics and Genomics Versus Arthritis, Centre for Musculoskeletal Research, Faculty of Biology, Medicine and Health, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. [Amos CI] Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas. [Miller FW, Rider LG] Environmental Autoimmunity Group, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH, Bethesda, Maryland. [Lundberg IE] Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, Solna, Karolinska Institutet, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden. [Gregersen PK] The Robert S. Boas Center for Genomics and Human Genetics, The Feinstein Institute, Manhasset, New York. [Selva-O'Callaghan A] Servei de Medicina Interna, Vall d’Hebron Hospital Universitari, Barcelona, Spain. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 36580032 |
| dc.identifier.wos | 000951145400001 |
| dc.rights.accessrights | info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess |

 Área privada
Área privada Contacto
Contacto